Capital Gain Tax
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/u852199908/domains/sskfinsol.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/elementor-pro/modules/nav-menu/widgets/nav-menu.php on line 1453
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/u852199908/domains/sskfinsol.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/elementor-pro/modules/nav-menu/widgets/nav-menu.php on line 1466
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/u852199908/domains/sskfinsol.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/elementor-pro/modules/nav-menu/widgets/nav-menu.php on line 1477
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/u852199908/domains/sskfinsol.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/elementor-pro/modules/nav-menu/widgets/nav-menu.php on line 1490
Menu
Capital Gain Tax

Any profit or gain that arises from the sale of a ‘capital asset’ is a capital gain. This gain or profit comes under the category ‘income’, and hence you will need to pay tax for that amount in the year in which the transfer of the capital asset takes place. This is called capital gains tax, which can be short-term or long-term.
Capital Asset means property of any kind, whether fixed or circulating, movable or immovable, tangible or intangible.
The table below shows the capital gain chargeable on various asset categories, short term or long term
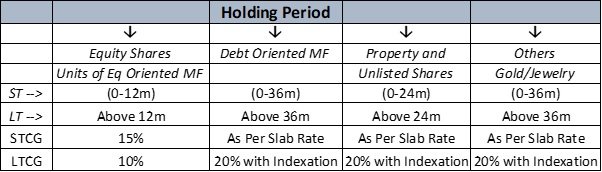
As you can see Equity as an Asset has better Tax efficiency as compare to others.
Another Important provision an Investor should know is the Exemption on Long Term Capital Gain
Capital Gain Exemption under Section 54 – when the capital gains from the sale of house property are reinvested into buying or constructing two another house properties, provided the capital gains do not exceed Rs. 2 crores. The new property can be purchased either one year before the sale or 2 years after the sale of the property. The exemption can be taken back if the new property is sold within 3 years from the date of purchase.
Section 54F – Exemption under Section 54F is available when there are capital gains from the sale of any asset other than a house property. You must invest the entire sale consideration and not only capital gain to buy a new residential house property to claim this exemption. Purchase the new property either one year before the sale or 2 years after the sale of the property.
Section 54EC – Exemption is available under Section 54EC when long term capital gains from sale of the first property are reinvested into specific bonds issued by National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) or Rural Electrification Corporation (REC). You can invest up to Rs 50 lakhs within 6 months from the date of transfer. The money invested can be redeemed only after 5 years.
Section 54B – You can avail exemption on Capital Gains from the sale of Land Used for Agricultural Purpose. The exempted amount is the investment in a new asset or capital gain, whichever is lower. You must reinvest into a new agricultural land within 2 years from the date of transfer.
Capital Gains Account Scheme – If capital gains have not been invested until the due date of filing of return (usually 31 July) of the financial year in which the property is sold, the gains can be deposited in a PSU bank or other banks as per the Capital Gains Account Scheme, 1988. This deposit can then be claimed as an exemption from capital gains, and no tax has to be paid on it. However, if the money is not invested, the deposit shall be treated as a short-term capital gain in the year in which the specified period lapses.
You can reduce your payable tax by arranging your investments within the various benefits offered under Income Tax Act 1961 in form of various exemptions and deductions but need to be careful as some of the investments may reduce your returns drastically.
